PermeaPad
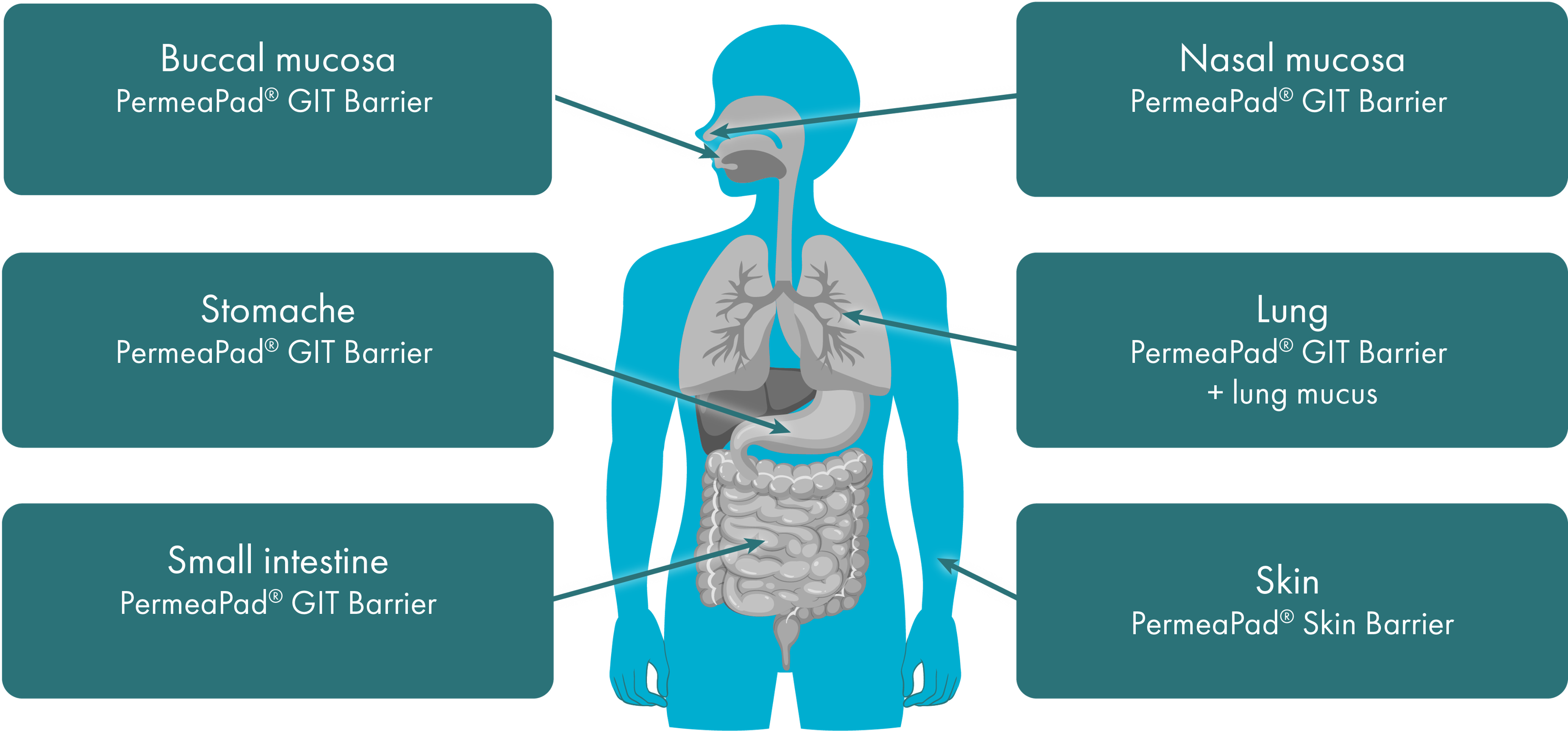
nasal mucosa
-
Drug delivery to the brain: In situ gelling for...
The objective of this work was to optimize a thermosensitive in situ gelling formulation to improve intranasal and nose-to-brain delivery of the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine (CBZ). A preliminary procedure of vehicles obtained just...
Drug delivery to the brain: In situ gelling for...
The objective of this work was to optimize a thermosensitive in situ gelling formulation to improve intranasal and nose-to-brain delivery of the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine (CBZ). A preliminary procedure of vehicles obtained just...
-
Human Lactobacillus Biosurfactants as Natural E...
"The inclusion of a chemical permeation enhancer in a dosage form is considered an effective approach to improve absorption across the nasal mucosa. Herein we evaluated the possibility of exploiting...
Human Lactobacillus Biosurfactants as Natural E...
"The inclusion of a chemical permeation enhancer in a dosage form is considered an effective approach to improve absorption across the nasal mucosa. Herein we evaluated the possibility of exploiting...
-
Interpreting non-linear drug diffusion data: Ut...
"The aim of this work was to clarify the dynamics behind the influence of ionic strength on the changes in drug release from large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs). For this purpose, we...
Interpreting non-linear drug diffusion data: Ut...
"The aim of this work was to clarify the dynamics behind the influence of ionic strength on the changes in drug release from large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs). For this purpose, we...
oral mucosa
-
Permeability of triamcinolone acetonide, releas...
The permeability of triamcinolone acetonide (TA), from bilayer mucoadhesive buccal films, through a biomimetic membrane, Permeapad™, was investigated employing Franz diffusion cell. The delivery systems composition and ethyl cellulose (EC) backing layer, on drug...
Permeability of triamcinolone acetonide, releas...
The permeability of triamcinolone acetonide (TA), from bilayer mucoadhesive buccal films, through a biomimetic membrane, Permeapad™, was investigated employing Franz diffusion cell. The delivery systems composition and ethyl cellulose (EC) backing layer, on drug...
-
In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of tas...
This study reports the development and characterization of taste masked, freeze-dried composite wafers for potential oral and buccal delivery of low dose aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) to prevent thrombosis in elderly patients with...
In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of tas...
This study reports the development and characterization of taste masked, freeze-dried composite wafers for potential oral and buccal delivery of low dose aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) to prevent thrombosis in elderly patients with...
-
Use of Permeapad® for prediction of buccal abso...
The present work explores the usefulness of Permeapad® for prediction of buccal absorption. Permeability studies with the model drug metoprolol were carried out using the Permeapad® barrier at pH values 7.4; 8.5; 9.0,...
Use of Permeapad® for prediction of buccal abso...
The present work explores the usefulness of Permeapad® for prediction of buccal absorption. Permeability studies with the model drug metoprolol were carried out using the Permeapad® barrier at pH values 7.4; 8.5; 9.0,...
Gastrointestinal tract
View all-
Comparison of in vitro screening methods for ev...
The effects of pharmaceutical excipients on intestinal drug absorption have been highlighted and careful excipient selection is required to develop biologically equivalent formulations. This study aimed to evaluate the effects...
Comparison of in vitro screening methods for ev...
The effects of pharmaceutical excipients on intestinal drug absorption have been highlighted and careful excipient selection is required to develop biologically equivalent formulations. This study aimed to evaluate the effects...
-
Shifting the Focus from Dissolution to Permeati...
In response to the growing ethical and environmental concerns associated with animal testing, numerous in vitro tools of varying complexity and biorelevance have been developed and adopted in pharmaceutical research and development....
Shifting the Focus from Dissolution to Permeati...
In response to the growing ethical and environmental concerns associated with animal testing, numerous in vitro tools of varying complexity and biorelevance have been developed and adopted in pharmaceutical research and development....
-
Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Pe...
Riluzole (RLZ), a sodium channel-blocking benzothiazole anticonvulsant BCS class II drug, is very slightly soluble in aqueous medium. To improve aqueous solubility and modulate dissolution rate and membrane permeability, complex...
Controlling the Solubility, Release Rate and Pe...
Riluzole (RLZ), a sodium channel-blocking benzothiazole anticonvulsant BCS class II drug, is very slightly soluble in aqueous medium. To improve aqueous solubility and modulate dissolution rate and membrane permeability, complex...
Lung mucosa
-
Permeability Assessment of a High-Throughput Mu...
Permeability across cellular membranes is a key factor that influences absorption and distribution. Before absorption, many drugs must pass through the mucus barrier that covers all the wet surfaces of...
Permeability Assessment of a High-Throughput Mu...
Permeability across cellular membranes is a key factor that influences absorption and distribution. Before absorption, many drugs must pass through the mucus barrier that covers all the wet surfaces of...
skin
-
Validation and testing of a new artificial biom...
Human skin remains the most reliable model for studying the transdermal permeation of active compounds. Due to the limited source, porcine skin has been used extensively for performing penetration tests. Performing penetration...
Validation and testing of a new artificial biom...
Human skin remains the most reliable model for studying the transdermal permeation of active compounds. Due to the limited source, porcine skin has been used extensively for performing penetration tests. Performing penetration...
General information
-
Commercially Available Cell-Free Permeability T...
Replacing in vivo with in vitro studies can increase sustainability in the development of medicines. This principle has already been applied in the biowaiver approach based on the biopharmaceutical classification...
Commercially Available Cell-Free Permeability T...
Replacing in vivo with in vitro studies can increase sustainability in the development of medicines. This principle has already been applied in the biowaiver approach based on the biopharmaceutical classification...
-
Drug permeability profiling using cell-free per...
Cell-free permeation systems are gaining interest in drug discovery and development as tools to obtain a reliable prediction of passive intestinal absorption without the disadvantages associated with cell- or tissue-based permeability profiling....
Drug permeability profiling using cell-free per...
Cell-free permeation systems are gaining interest in drug discovery and development as tools to obtain a reliable prediction of passive intestinal absorption without the disadvantages associated with cell- or tissue-based permeability profiling....
-
'Stirred not Shaken!' Comparing Agitation Metho...
In order to achieve a high sample throughput, permeation experiments are often carried out using 96-well sandwich plates. Even though agitation is regarded as important, permeation studies in 96-well format...
'Stirred not Shaken!' Comparing Agitation Metho...
In order to achieve a high sample throughput, permeation experiments are often carried out using 96-well sandwich plates. Even though agitation is regarded as important, permeation studies in 96-well format...
